In the future hyperproductivity will be possible thanks to technological advancement, for example by the improvement of artificial intelligence to better support human labour.
In this scenario a hyperproductive section of the population looks after the well-being of everyone else. But it is important to find out to what extent it will be possible to provide everyone with the opportunity to be hyperproductive.
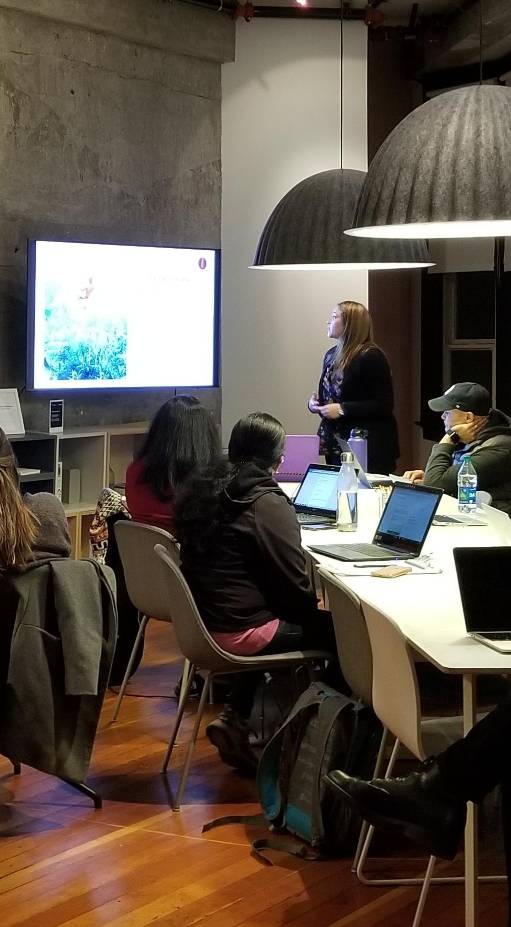
In the future meritocracy will be based on productivity differences in working life and being able to most accurately demonstrate them. Hyperproductive workers will be elevated to serve globally competing companies and the added value they produce will be many times higher compared to the average worker.
The time of merited individuals will be used extremely efficiently for solving difficult problems. But if on the one hand, the elites are committed to the development of society and are accountable to society for their actions, on the other hand, putting hyperproductive individuals in the spotlight can also lead to individualization of success, as well as growth income inequality.